The next generation of telecom networks (fifth generation or 5G) started hitting the market at the end of 2018 and will continue to expand worldwide. Beyond speed improvement, the technology is expected to unleash a massive 5G IoT (Internet of Things) ecosystem where networks can serve communication needs for billions of connected devices, with the right trade-offs between speed, latency, and cost.
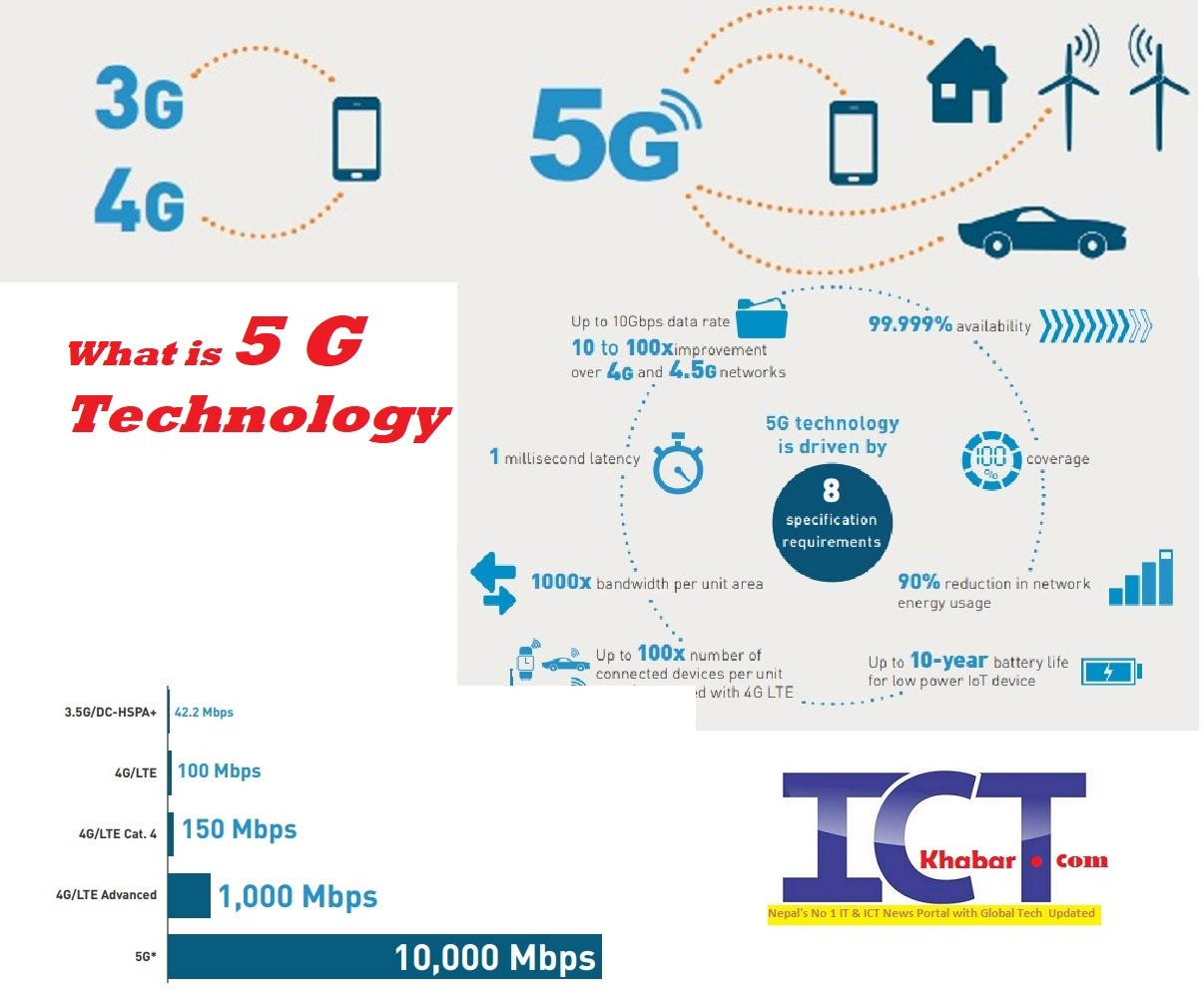
5G technology is driven by 8 specification requirements
Up to 10Gbps data rate - > 10 to 100x speed improvement over 4G and 4.5G networks
1-millisecond latency
1000x bandwidth per unit area
Up to 100x number of connected devices per unit area (compared with 4G LTE)
99.999% availability
100% coverage
90% reduction in network energy usage
Up to 10-year battery life for low-power IoT device
Emerging 5G networks feature lower latency, higher capacity, and increased bandwidth compared to 4G. These network improvements will have far-reaching impacts on how people live, work, and play all over the world. Emerging 5G networks feature lower latency, higher capacity, and increased bandwidth compared to 4G.
5G transition is so complicated, and because we've been having a pandemic for two years, this time the shift may take even longer. Scientists in Finland who helped developed 5G technology say that it may be 2027 before we see the robotics, smart objects, and augmented reality we're been promised.
For now, the first big 5G application is a 30-year-old idea: home internet service. T-Mobile and Verizon are using their 5G networks to better compete with cable home internet, adding some competition into a very uncompetitive realm.
However,5G download speed may differ widely by area.
According to the February 2020 issue of Fortune Magazine, average 5G speed measures done in Q3/Q4 2019 range from:
220 megabits per second (Mbps) in Las Vegas,
350 in New York,
380 in Los Angeles,
450 in Dallas,
to 550 Chicago,
and over 950 in Minneapolis and Providence, approximately.
That's 10 to 50 times more than 4G LTE.
5G speed can vary widely based on your proximity to a 5G tower and the surrounding environment. Close to a 5G tower with a clear line of sight, you could experience speeds surpassing 1000 Mbps—nearly tenfold the rates of 4G. However, these speeds can diminish as the distance from the tower increases or if obstacles interfere with the signal.















